In this article, we will delve into the intriguing history of the Etruscans, one of antiquity’s most captivating civilizations that inhabited the Italian peninsula. If you’re a history buff planning to visit Italy, keep reading to uncover more about this enigmatic civilization.
Table of Contents
Who were the Etruscans?
The Etruscans are among the ancient populations that lived in Italy and are considered one of the greatest civilizations of the past. The origin of the Etruscans is still a topic of debate among scholars, with theories pointing to Asia Minor, Northern Europe, or even the Villanovians as possible ancestors.
The Etruscan civilization began to develop around the start of 800 B.C., but many aspects of this civilization, such as its language, remain unknown.
You can check out a map of all the Etruscan museums in Italy at this link.
Where did the Etruscans, the enigmatic pre-Roman civilization, live?
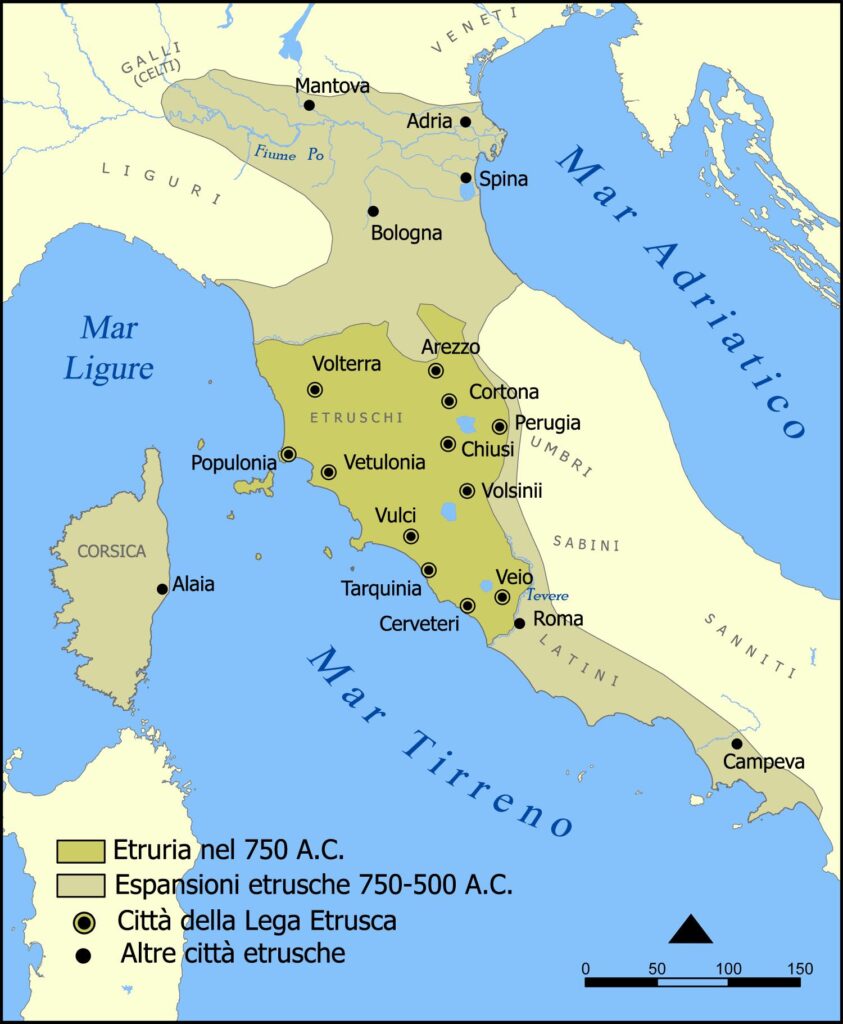
Initially, the Etruscans occupied the region called Etruria, which corresponds to parts of present-day Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, living in villages on the banks of lakes and rivers.
Around 700 B.C., they began to build sturdier houses on hilltops, giving rise to the first cities.
From there, the Etruscan civilization expanded its domains over a vast area of the Italian peninsula, including part of the Padana Plain and present-day Campania.
Some of the cities founded by the Etruscans include Arezzo, Volterra, Perugia, Bologna (then called Felsina), Mantua, Capua, Nola, Pompeii, and Sorrento.
There’s also a theory that the name Florence has Etruscan origins, read more about it in this article.
If you enjoy walking, you can traverse the Via degli Dei in Mugello on foot: it was an ancient path used by the Etruscans!
When did the Etruscan civilization develop?
The height of the Etruscan civilization occurred between 700 B.C. and 500 B.C., a period during which they allied with the Phoenicians to challenge Greek dominance in the Tyrrhenian Sea.
The Etruscan decline began in 396 B.C., when the Romans conquered the city of Veii.
Subsequently, the Romans subjugated all Etruscan territories, which, from 200 B.C., became part of the domains of Rome.
Tip in Tuscany: in Chianciano Terme, after visiting the thermal baths, take the opportunity to visit the Chianciano Terme Etruscan Museum.
What activities did the Etruscans engage in?
The Etruscan territory was predominantly mountainous, and in these areas, they cultivated olive trees and vines.
They also carried out drainage works in swampy areas and deforestation to increase the cultivable areas, obtaining wood to build their houses and ships, and creating more space for the cultivation of cereals, fruit trees, and vegetables.
The Etruscans also raised pigs, sheep, and cattle, and fishing was common.
The principal wealth of Etruria, however, came from the presence of metals in the subsoil: copper and lead in the metalliferous hills, and iron on the island of Elba. Using these metals, Etruscan artisans crafted agricultural tools and weapons, and combined them with silver to produce refined filigree objects.
Etruscan potters, merging charcoal and clay, created a black pottery called bucchero, utilized in the making of vessels.
Planning on visiting the Tuscan coast? Be sure to include a visit to the Isidoro Falchi Museum in Vetulonia and see firsthand some of the objects that belonged to the Etruscans. Read more about it here.
The abundance of raw materials, products manufactured by Etruscan artisans, and proximity to the Tyrrhenian Sea fueled commercial activities. The Etruscans built a prosperous merchant fleet that transported their products throughout the Mediterranean, becoming a maritime power.
How was Etruscan society organized?
Etruscan society comprised aristocratic families of landowners, who owned almost all the cultivable land, and wealthy merchants.
The aristocrats led a comfortable life, enjoying feasts, music, and dancing.
Warriors and priests were prosperous and played a significant role in society.
Artisans and small traders managed to enrich themselves thanks to the expansion of commerce.
Most of the population was composed of workers such as peasants, laborers, and small artisans, who worked in the service of the aristocrats. At the bottom rung of society were the slaves, who primarily worked in the mines and had no rights.
What was the role of Etruscan women?
Etruscan women, unlike Greek and, to some extent, Roman women, were not confined to domestic activities but also played a significant social role. They could partake in banquets alongside their husbands and even intervene, albeit indirectly, in political matters.
What was everyday life like for the Etruscans?
Archaeological discoveries in the tombs of aristocratic families allow us to understand the most significant aspects of Etruscan daily life. In these tombs, which resemble houses, frescoes and everyday objects were found. The frescoes often depict Etruscans enjoying feasts, participating in sports events, listening to music, and dancing.
What did the Etruscan people eat?
Thanks to the frescoes found in the tombs, we know that the wealthier Etruscans served meat, poultry, fruits, bread, eggs, and focaccia at the table. However, the main food of the population was wheat, followed by vegetables, hams, and cheeses obtained from goat milk.
Olive oil was the most widely used condiment, and the most consumed drink was wine. In coastal cities, fish was the main food.
What was the religion of Etruscan society?
The Etruscans were polytheistic, and religion played a significant role in their lives. They believed that gods communicated with humans through natural phenomena like thunder, lightning, and even the flight of birds.
The interpretation of divine messages was entrusted to specific priests, called augurs. The haruspices practiced divination, claiming they could predict the future by observing the internal organs of animals sacrificed to the gods.
How were funerals conducted and where did the Etruscans bury their dead?
The Etruscans believed in life after death and dedicated great care to the cult of the dead, as evidenced by the many necropolises, the “cities of the dead”. In the necropolises, tombs of different types can be found, depending on the period they were built and the social status of the deceased.
Some tombs are carved into rock, resembling dwellings, complete with rooms, furniture, and everyday objects, giving them the name “house tombs“. Other tombs were built above ground and are known as “tumuli”, or burial mounds. These tombs often held multiple burials and were for wealthier individuals or families.
The tombs of the most affluent Etruscans resembled small-scale replicas of Etruscan homes, complete with murals that depicted scenes from the life of the deceased. The interiors of these tombs featured carved stone furniture, such as beds and chairs, meant to provide comfort for the deceased in the afterlife.
These burial practices indicated a belief in an afterlife, where the deceased could continue to enjoy the comforts and pleasures of their earthly existence.
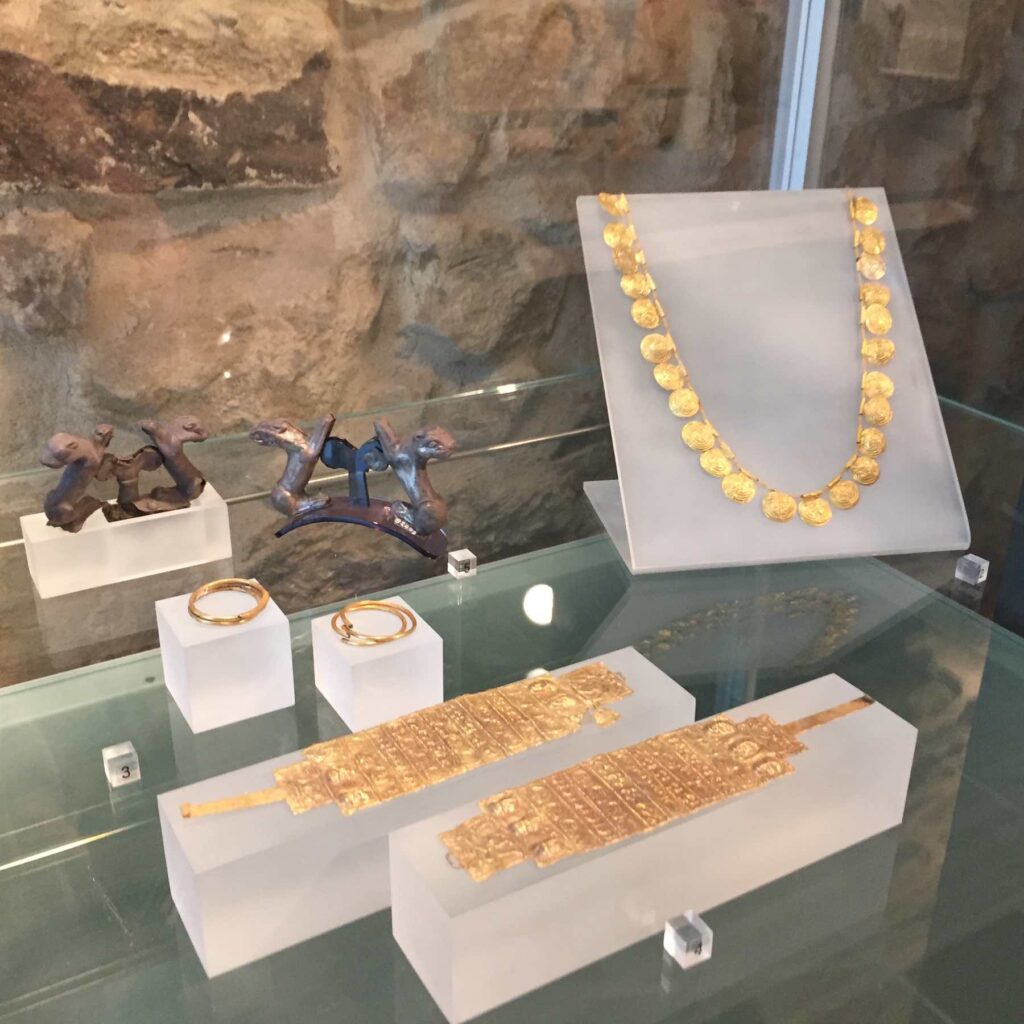

The tombs were filled with a variety of grave goods, including pottery, jewelry, tools, and weapons. These items were believed to be useful to the deceased in their journey to the afterlife. They also serve as a rich source of information for modern archaeologists, providing insight into the daily life, beliefs, and social structure of the Etruscans.
Video
Below, I share a video I found online that provides a good overview of the Etruscans.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Etruscans were an advanced civilization known for their metalworking, maritime trading, and rich social structure.
Their unique burial practices and the artifacts found within their tombs offer a fascinating glimpse into their belief in the afterlife and their daily lives.
Despite being absorbed into the Roman Empire, their influence can still be seen today in the region of Tuscany and throughout Italy.
Enjoyed the tip? By booking through our links, you support Tuscany.Tips and help us keep sharing valuable content like this – at no extra cost to you.
FIND YOUR NEXT STAY
Book your stay in Italy or anywhere in the world with our partner Booking.com!
You'll find the best deals and support our website. Thank you!
BOOK TRANSFERS AND TOURS ONLINE
Book transfers, tours, and excursions in Italy and around the world with our partner Get Your Guide.
NEED DATA IN ITALY?
Get 5% off your Holafly eSIM with code TIPS—fast, easy, and reliable!





